Types of computer security risks and Security measure
SECURITY MEASURE
What is security measure?




What is security measure?
The precautionary measures taken toward possible danger or damage.
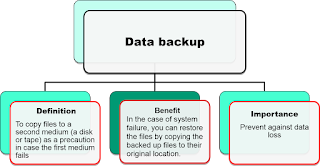
DATA BACKUP
•A data backup is the result of copying or archiving files and folders for the purpose oF
being able to restore them in case of data loss.
•Data loss can be caused by many things ranging from computer viruses, hardware
failures, file corruption, system failure or theft.
•If you are responsible for business data, a loss may involve critical financial, customer,
and company data.
•If the data is on a personal computer, you could lose financial data and other key files,
pictures, music and others that would be hard to replace.

CRYPTOGRAPHY
*Cryptography is technology of encoding information so it can only be read by authorized
individuals.
*Encryption is process of converting readable data into unreadable characters to
prevent unauthorized access.
*Decryption is process to recorded encrypted data.

How…
-To read the data, you must decrypt it into readable form.
-The unencrypted data is called plain text.
-The encrypted data is called cipher text.
-To encrypt, plain text converted into cipher text using an encryption key.
Importance…
-The process of proving one's identity.
-Ensuring that no one can read the message except the intended receiver.
-Assuring the receiver that the received message has not been altered in anyway
from the original.
-A mechanism to prove that the sender really sent this message.
ANTI-VIRUS
•Anti-virus software is a program or set of programs that are designed to
prevent, search for, detect and remove software viruses and other malicious software
like worms, Trojan horses, adware and more.
•If and when a virus is detected, the computer displays a warning asking
what action should be done, often giving the options to remove, ignore, or move the file to
the vault.
•If a virus infected a computer without an antivirus program, it may delete
files, prevent access to files, send spam, spy on you, or perform other
malicious actions.
•Examples: Norton anti-virus, AVG anti-virus, Kaspersky anti-virus

ANTI-SPYWARE
•Anti-spyware is a type of software that is designed to detect and remove unwanted
spyware programs.
•Anti-spyware software can be used to find and remove spyware that has already been
installed on the user's computer.
•OR it can act much like an anti-virus program by providing real-time protection and
preventing spyware from being downloaded in the first place.
•Examples :
-Spyware Blaster
-Spy Sweeper

FIREWALL
•A firewall is a system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private
network.
•A firewall can be implement either through hardware or software form, or a combination
of both.
•Firewalls prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing private networks
connected to the Internet, especially intranets.
•All messages entering or leaving the intranet (i.e., the local network to which you are
connected) must pass through the firewall, which examines each message and blocks those
that do not meet the specified rules/security criteria.
•Rules will decide who can connect to the internet, what kind of connections can be made,
which or what kind of files can be transmitted in out.

PHYSICAL ACCES CONTROL
•Lock your laptop whether you're at home, in a dorm, in an office, or sitting in a coffee
shop, use a security device, such as a laptop security cable.
•Lock doors and windows, usually adequate to protect the equipment.
•Put the access code at the door to enter the computer room or your office.
•Put the CCTV (closed-circuit television) in your office or computer room.
•Make a policies who can access the computer room or your data center.
COMPUTER SECURITY RISK
Definition of computer security risk:
Any event or action that could cause a loss of or damage to computer hardware, software, data, information or processing capability.
MALICIOUS CODE
•Malicious code is code causing damage to a computer or system. It is code not easily or
solely controlled through the use of anti-virus tools.
•Malicious code can either activate itself or be like a virus requiring user to perform an
action, such as clicking on something or opening an email attachment.
*Computer Virus
•Definition : A computer virus is a potentially damaging computer program that affects or
infects, a computer negatively by altering the way the computer works without the user’s
knowledge or permission.
•A computer virus attaches itself to a program or file enabling it to spread from one
computer to another, leaving infections as it travels
•It may damage files and system software, including the operating system.
*Worm
•A worm is a program that copies itself repeatedly.
•For example in memory or on a network, using up resources and possiblyshutting down
the computer or network.
•Worms spread from computer to computer, but unlike a virus, it has the capability to travel
without any human action.
*Trojan Horse
•A program that hides within or looks like a legitimate program. It does not replicate itself to
other computers.
•At first glance will appear to be useful software but will actually do damage once installed
or run on your computer.
•Examples: It can change your desktop, adding silly active desktop icons or they can cause
serious damage by deleting files and destroying information on your system.
•Examples: Netbus, Back Orifice, Subseven, Beast
UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS & USE
•To help prevent unauthorized access and use, they should have a written acceptable use
policy (AUP) that outlines the computer activities for which the computer and network may
and may not be used.
•An access control is a security measure that defines who can access a computer, when
they can access it, and what actions they can take while accessing the computer.
•Many systems implement access controls using a two-phase process called identification
and authentication.
•Identification verifies that an individual is a valid user.
HARDWARE THEFT
•Hardware theft is the act of stealing computer equipment.
•Hardware vandalism is the act of defacing or destroying computer equipment.
•Companies, schools, and other organizations that house many computers, however, are at
risk of hardware theft.
•Safeguards against Hardware Theft and Vandalism:
-physical access controls, such as locked doors and windows
-install alarm systems in their buildings
-physical security devices such as cables that lock the equipment to a desk.
SOFTWARE THEFT
•Software theft occurs when someone:
-Steals software media
-Intentionally erases programs
-Illegally copies a program
-Illegally registers and/or activates a program.
•Steals software media involves a perpetrator physically stealing the media that contain the
software or the hardware that contains the media.
•Intentionally erases programs can occur when a programmer is terminated from, or stops
working for a company.
•Although the programs are company property, some dishonest programmers intentionally
remove or disable the programs they have written from company computers.
INFORMATION THEFT
•Information theft occurs when someone steals personal or confidential information.
•If stolen, the loss of information can cause as much damage as (if not more than) hardware
or software theft.
•An unethical company executive may steal or buy stolen information to learn about a
competitor.
•A corrupt individual may steal credit card numbers to make fraudulent purchases.
SYSTEM FAILURE
•A system failure is the prolonged malfunction of a computer.
•Can cause loss of hardware, software, data, or information.
•These include aging hardware; natural disasters such as fires, floods, or hurricanes;
random events such as electrical power problems; and even errors in computer programs.




Comments
Post a Comment